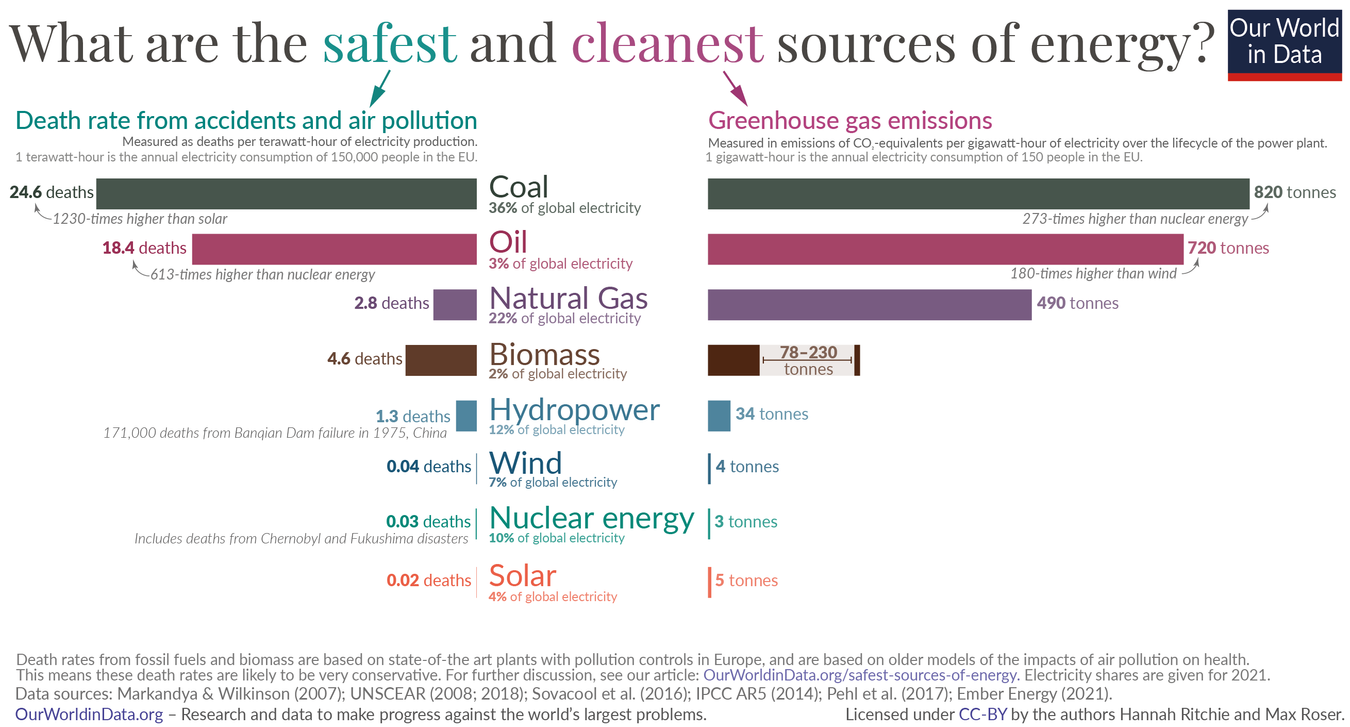
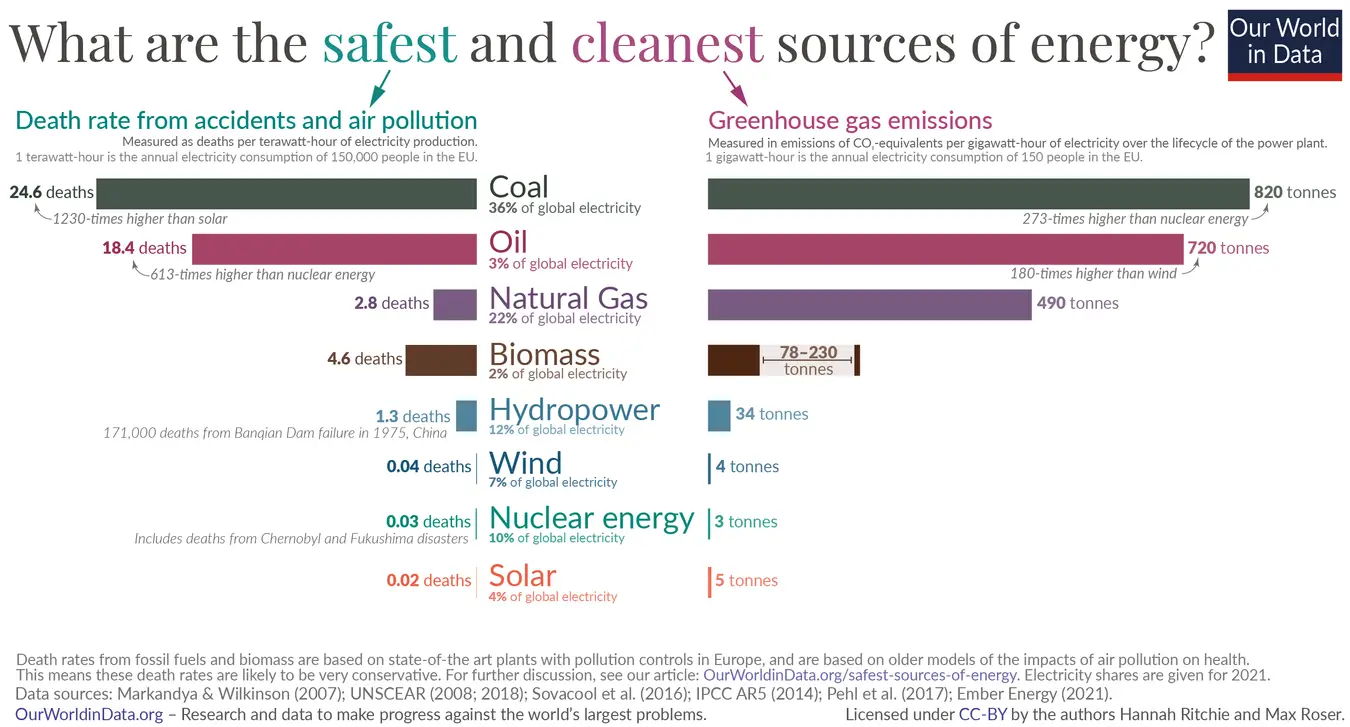
Nuclear Energy Africa: The continent of Africa is at a pivotal moment in its energy evolution. As demand for electricity surges alongside rapid industrialization and urbanization, African leaders are looking toward nuclear energy as a transformative solution. The Nuclear Energy Innovation Summit for Africa (NEISA 2025), held in Kigali, Rwanda, has highlighted the urgent need for accelerating nuclear energy adoption to meet the continent’s growing power needs sustainably. This shift promises to not only fuel economic growth but also drive industrial development and help achieve long-term sustainability goals.
1. Meeting Africa’s Growing Energy Demand
With a population expected to double by 2050, Africa faces unprecedented energy challenges. Traditional energy sources have struggled to keep pace with rising demand, resulting in frequent power shortages and hampered economic activities. Nuclear energy offers a reliable and scalable power option that can generate large quantities of electricity with minimal carbon emissions. Summit participants emphasized that embracing nuclear technology is essential to close the energy gap, ensure grid stability, and support the expanding needs of industries and households across diverse regions.
2. Nuclear Energy Africa: Supporting Industrialization Through Clean Power
Industrial growth requires stable, high-capacity energy supplies. Nuclear energy provides a consistent and clean source of power critical for manufacturing, mining, and other energy-intensive sectors. African leaders at NEISA 2025 underscored how nuclear adoption can propel industrialization, creating jobs and fostering economic diversification. By integrating nuclear power into national grids, countries can attract investments and build competitive industries aligned with global sustainability standards.
3. Nuclear Energy Africa: Driving Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
The continent’s commitment to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals includes expanding access to affordable and clean energy (SDG 7) and taking urgent action to combat climate change (SDG 13). Nuclear energy’s low greenhouse gas emissions make it a key component in Africa’s climate strategy. Delegates at the summit discussed how nuclear power aligns with sustainable development frameworks, helping countries reduce carbon footprints while promoting inclusive growth and energy equity.
4.Nuclear Energy Africa: Building Regional Cooperation and Capacity
Implementing nuclear energy programs requires significant technical expertise and regulatory frameworks. African nations are collaborating to develop shared knowledge bases, safety standards, and training centers to build capacity. The summit highlighted partnerships among governments, regional bodies, and international organizations to pool resources and harmonize policies. Such cooperation ensures safe, responsible nuclear energy deployment tailored to Africa’s unique contexts and challenges.
5. Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Safety
Despite its benefits, nuclear energy adoption faces hurdles including high initial costs, public perception concerns, and regulatory complexities. Summit delegates stressed the importance of transparent communication and robust safety protocols to build public trust. Investments in research, infrastructure, and governance are critical to address risks and ensure that nuclear energy contributes positively to Africa’s development trajectory.

6. Driving Innovation with Advanced Nuclear Technologies in Africa
Emerging nuclear technologies, such as small modular reactors (SMRs), are reshaping the feasibility of nuclear energy adoption across Africa. These reactors offer enhanced safety features, reduced construction times, and lower upfront costs compared to traditional large-scale plants. By embracing such innovations, African countries can overcome infrastructure and grid challenges, enabling a more flexible and scalable energy supply. This technological progress aligns perfectly with the continent’s ambitions for sustainable industrial growth and energy independence.
7. Boosting Economic Growth and Employment Opportunities
The expansion of nuclear energy infrastructure not only ensures reliable power but also generates significant economic benefits. Construction, operation, and maintenance of nuclear facilities create diverse employment opportunities for skilled professionals and local communities. Additionally, a stable power supply attracts foreign investment and stimulates industrial sectors critical for Africa’s economic diversification. Summit discussions highlighted that investing in nuclear energy could be a catalyst for broad-based economic development across the continent.
8. Nuclear Energy’s Role in Meeting Climate Goals
Africa’s commitment to tackling climate change includes diversifying its energy portfolio with low-carbon alternatives. Nuclear power, with its near-zero greenhouse gas emissions, complements renewable sources like solar and wind by providing consistent base-load electricity. This balanced energy mix is essential for reducing reliance on fossil fuels while ensuring grid stability. Leaders at NEISA 2025 emphasized nuclear energy’s crucial role in helping Africa meet its environmental commitments and global climate targets.
9. Enhancing Energy Security and Sovereignty
By developing indigenous nuclear energy capabilities, African countries can significantly reduce dependence on imported fuels and volatile global energy markets. Nuclear power offers a steady, domestically controlled electricity source that bolsters national energy security. This autonomy is vital for ensuring uninterrupted power to industries, businesses, and households, ultimately supporting resilient economic and social development.
10. Establishing Robust Policies and International Cooperation
Successful nuclear energy programs require comprehensive policy frameworks, regulatory oversight, and adherence to safety standards. African nations are collaborating to harmonize regulations and share best practices, supported by partnerships with international agencies such as the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). These cooperative efforts help ensure the safe, responsible, and transparent deployment of nuclear technology across the continent.
11. The Role of Education and Workforce Development in Nuclear Energy Africa
Developing a skilled workforce is essential for the successful adoption and sustainable operation of nuclear energy across Africa. Educational institutions and vocational training centers are increasingly incorporating nuclear science and engineering into their curricula to prepare the next generation of experts. Scholarships, internships, and partnerships with international nuclear organizations provide aspiring professionals with hands-on experience and exposure to global best practices. Investing in human capital ensures that African countries not only build nuclear plants but also maintain high safety and efficiency standards over the long term.
12. Community Engagement and Public Perception of Nuclear Energy Africa
Public acceptance is a critical factor for the deployment of nuclear energy projects. In many African communities, concerns about nuclear safety, environmental impacts, and radiation risks persist. Effective community engagement campaigns aim to educate the public about the benefits and risks of nuclear power, dispel myths, and involve local stakeholders in decision-making processes. Transparent communication builds trust and fosters a supportive environment for nuclear infrastructure development. This dialogue is vital to ensuring that nuclear energy initiatives align with social values and community needs.
13. Financing and Investment Strategies for Nuclear Energy Africa
Securing adequate financing for nuclear projects is one of the main challenges facing African countries. Nuclear plants require substantial upfront investments and long-term financial planning. Public-private partnerships, international development funds, and green financing mechanisms are being explored to bridge funding gaps. Innovative financing models, such as phased investments in small modular reactors, reduce risks for investors and governments alike. Transparent and sustainable investment strategies are crucial to unlocking the capital needed for nuclear energy to flourish across the continent.
14. Integrating Nuclear Energy Africa with Renewable Energy Sources
Nuclear energy is most effective when integrated within a diverse energy mix that includes renewables like solar, wind, and hydro power. Such integration enhances grid stability by balancing intermittent renewable generation with the reliable base-load capacity of nuclear power. African energy planners are designing hybrid systems that optimize resource use, reduce emissions, and improve energy access in rural and urban areas alike. This complementary approach maximizes the continent’s potential for a clean and resilient energy future.
Conclusion
The advancement of Nuclear Energy Africa marks a pivotal step towards sustainable development and energy resilience. With innovation, economic growth, and environmental stewardship at its core, nuclear power offers African nations a pathway to meet growing energy demands while fostering industrial progress and climate responsibility. Continued collaboration and investment will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of nuclear technology for the continent’s future.
Explore our detailed coverage on Renewable Energy Initiatives in Africa for further insights.
Source: AllAfrica